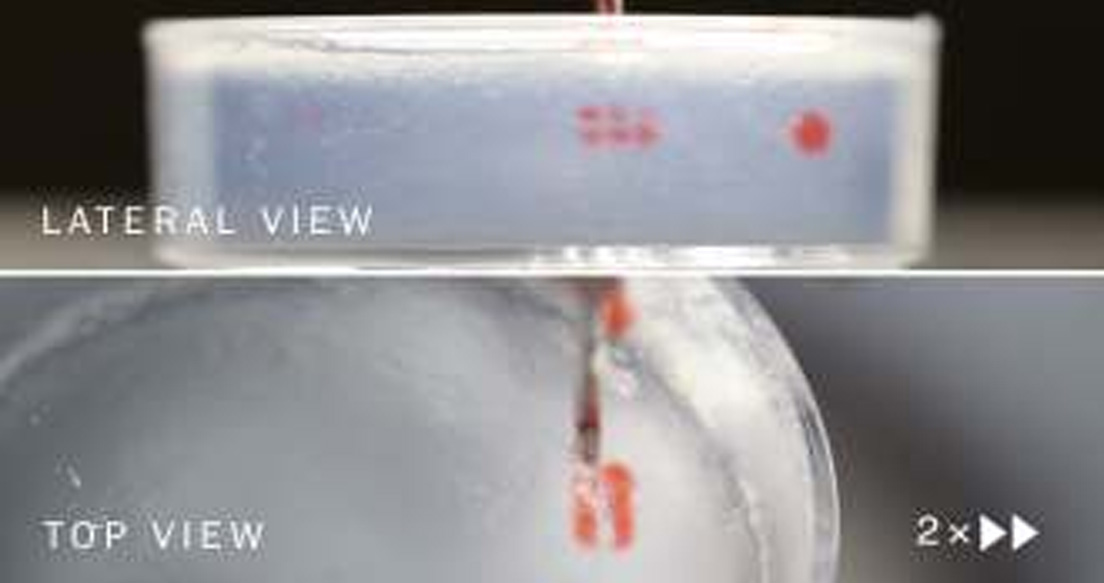
At the University of Virginia researchers developed a new bioprinting technique based on voxels. Voxels are 3D cubes that form basic building blocks in computer graphics, similar to what pixels are for 2D, and have been popularized by games such as Minecraft. The new technique involves printing discrete spherical blobs of bioink (as the voxels) within a supportive matrix that then swell to merge together, forming a porous structure. Sticky bioinks can be difficult to handle and print predictably, but…