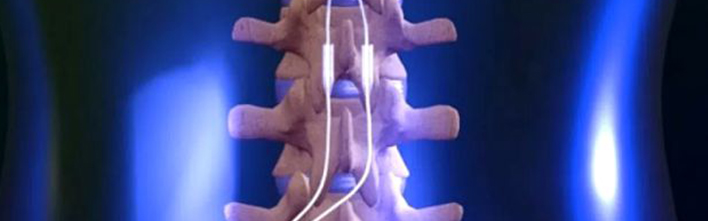
Boston Scientific Corporation announced positive results from the WHISPER randomized controlled trial (RCT). The data, presented at the 2018 Annual Meeting of the North American Neuromodulation Society in Las Vegas, demonstrated that patients who are given the choice to use both sub-perception and paresthesia-based spinal cord stimulation (SCS) therapy achieve superior outcomes in comparison to patients who have only one SCS therapeutic option.
SCS works by sending low electrical pulses, which vary in frequency, pulse width and amplitude, to the spinal cord to interrupt pain signals and provide pain relief. Paresthesia-based therapy provides pain relief with a light tingling sensation while sub-perception therapy works without that sensation. The WHISPER RCT is a multi-center, prospective, cross-over, randomized, and controlled study that evaluated the long-term safety and effectiveness of sub-perception SCS therapy. Participants had been implanted with an SCS system for an average of four years at the beginning of the study and were treated with both paresthesia and sub-perception therapy.
“The WHISPER RCT evaluated both patients who had successfully controlled their pain using SCS and those who could benefit from additional options and optimization of their therapy,” said James North, M.D., Carolinas Pain Institute, and coordinating principal investigator of the WHISPER RCT. “This study provides data on people who have suffered with chronic pain for years and who pose some of the biggest challenges in the long-term use of SCS. The results demonstrated that giving patients the choice to use sub-perception or paresthesia-based therapy provides superior patient outcomes and affirms that SCS is a clinically valuable treatment option.”