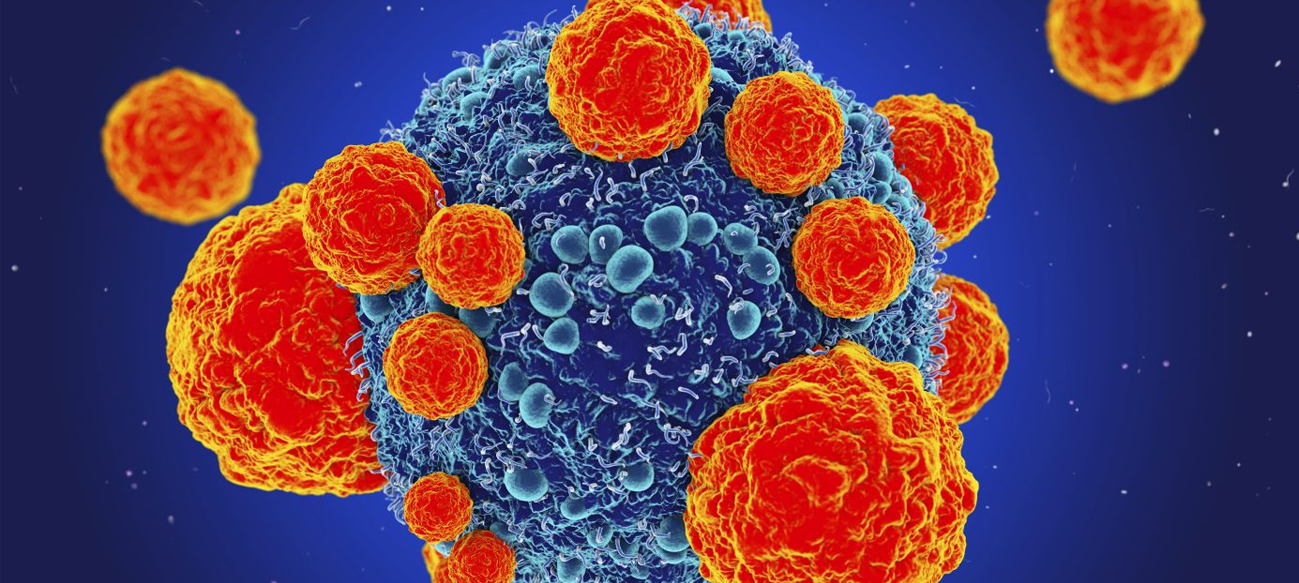
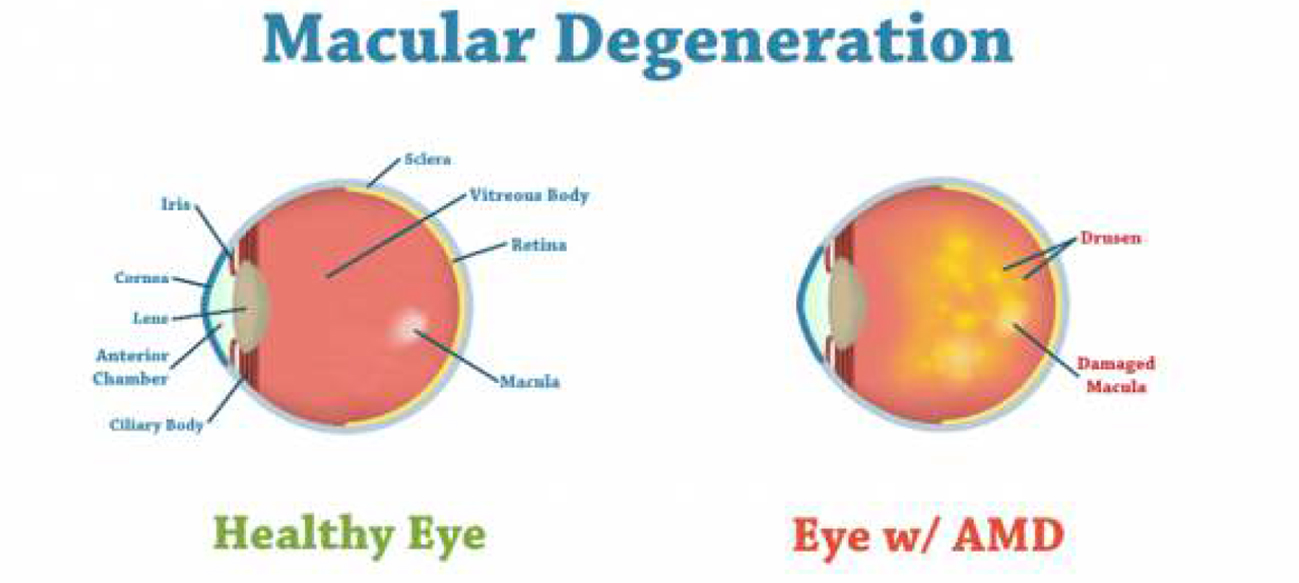
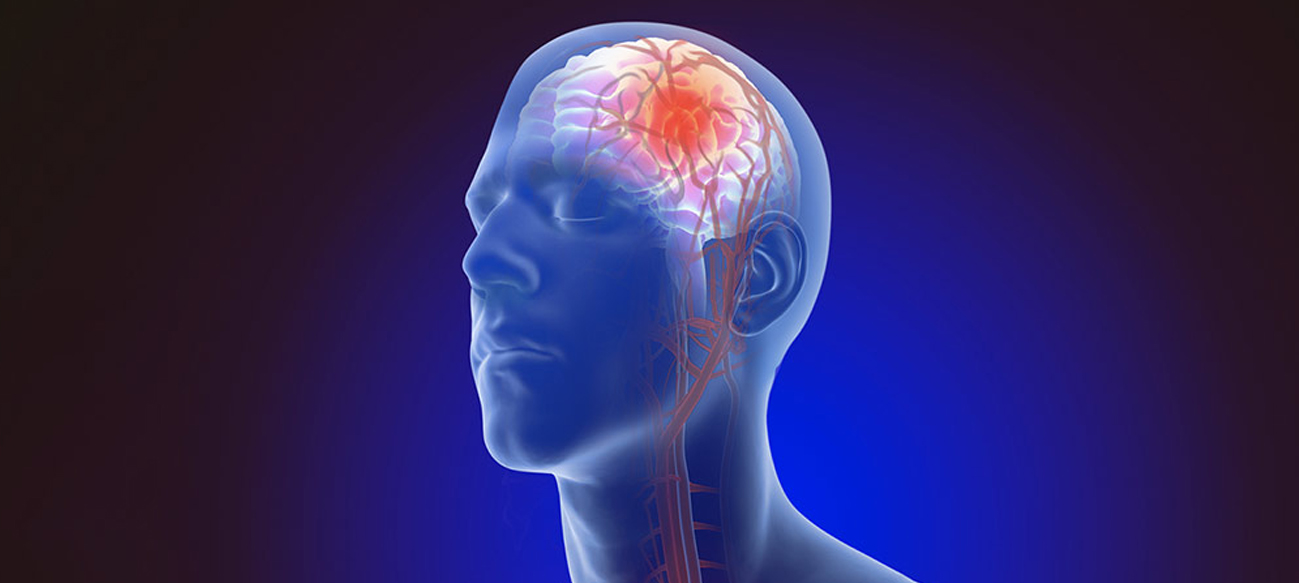
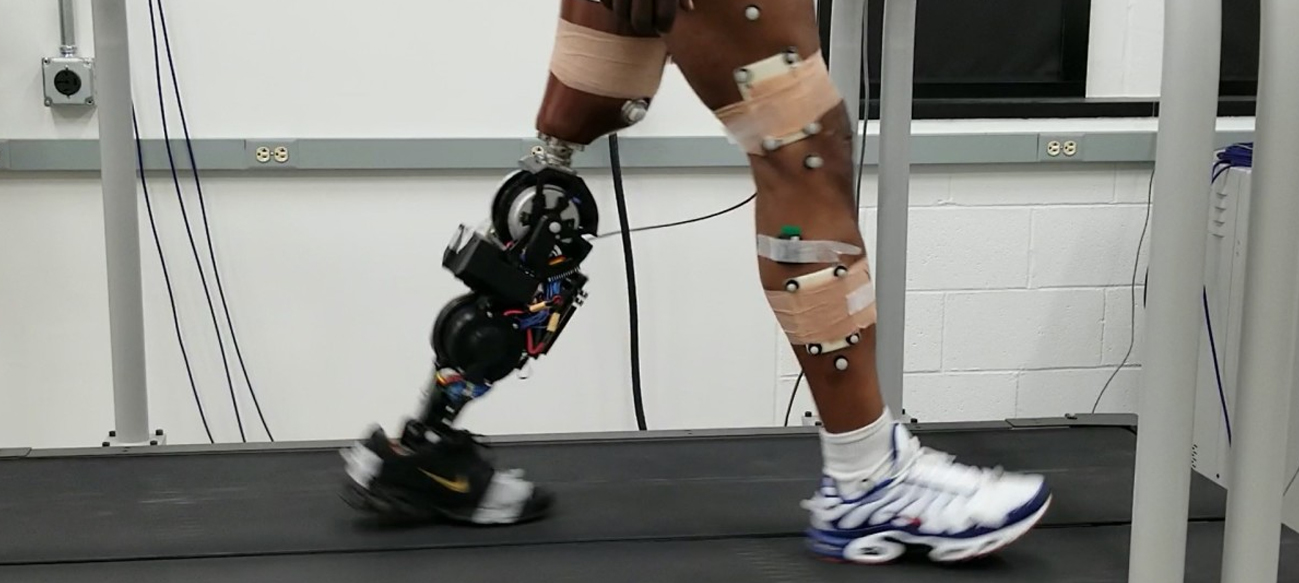
Researchers have demonstrated that a fatty acid called dihomogamma-linolenic acid, or DGLA, can kill human cancer cells. The study, published in Developmental Cell on July 10, found that DGLA can induce ferroptosis in an animal model and in actual human cancer cells. Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent type of cell death that was discovered in recent years and has become a focal point for disease research as it is closely related to many disease processes. Jennifer Watts, a Washington State University…